FAQs about Thin Clients
Almost every day, we receive questions regarding thin clients. We realized it is a topic over which there are many misunderstandings and common mistakes. In this article, you will find the most popular questions people ask themselves about thin clients, simply explained.
1. What is a thin client in non-technical layman terms?
A thin client is a device which is used to remotely connect to a server-based computing environment. Unlike a normal PC, a thin client doesn’t have any computing resources (applications, data & memory) locally. All of the computing resources are present on the server. So, a thin client is a device which runs on the computing resources present on the server. Thin clients generally come with very small hardware specs as the server does all of the computing work.
2. What is a thin client used for?
A thin client is used to access enterprise resources present on the remote server. “But you can do this with a normal PC right?” This is absolutely right. The real use of a thin client arises when it comes to security and managing them remotely without any effort, all while reducing energy consumption, electromagnetic waves, noise pollution, etc…, and increasing the hardware life span. Thin clients come with a read only OS. The user cannot modify any local configuration (installing an application, changing settings, etc…) which makes thin clients extremely secure. The remote management software provided with your thin client allows you to securely manage all of the thin clients remotely from anywhere. Imagine a company with 1000 endpoints, on which you need to apply a new template. You can perform this remotely, with just a few clicks, from your remote management tool. Click here if you are interested in knowing what more a thin client can offer.
3. What is the best thin client solution?
There is no “one size fits all solution”. It actually depends on what your needs are and what you want to accomplish using your thin client. There are some basic factors to be considered before buying a thin client. The list below will help you identify the best thin client option based on your needs.
- Hardware specifications of thin client (RAM, processor, etc)
- Physical peripheral support
- Multi monitor support & display input options (HDMI, DisplayPort, VGA & DVI)
- Will the chosen thin client serve all your needs up to 10 years?
- Which applications does the thin client support?
- In some cases, you can choose to repurpose your existing hardware into a thin client rather than investing in new hardware. Would this case apply to you?
- Does the remote management tool provided with the thin client cover all your needs?
- Does the thin client have Wi-Fi & Bluetooth?
This list is not exhaustive. If you are considering buying a thin client, here is a detailed blog on how to choose the best thin client solution.
4. How much does a thin client cost/ Are thin clients expensive/ Why are thin clients so expensive?
Thin clients generally start at $200 USD & the price increases with specifications. But the purchase price is not the only factor to consider. Thin clients help you save money in the long run as they are more secure, easier to manage, consume 10 times less energy than a PC, have no anti-virus, etc. This blog helps you understand why a thin client is cheaper than a PC in long run.
5. What are the applications of thick and thin clients?
Thick clients are used when all of the computing resources are present locally on the device itself. It might connect to the server when required but thick clients can completely work without connecting to a remote server. An example of thick clients are PCs. PCs do not need a server to work as the computing resources are present locally and they are highly customizable by the end user which makes them vulnerable to security risks. Thin clients are used exclusively to access remote resources on a distant server, using only a browser. A thin client cannot work without connecting to a server & it does not allow the end user to customize it, which makes it extremely secure. Besides security, it is extremely easy to manage and troubleshoot endpoints remotely.
6. How to install applications on a thin client?
Thin clients generally come with a management tool that makes it very easy to install, remove, update and manage applications remotely and securely. Click here to see what a powerful remote management tool is capable of.
7. Does thin clients support applications like Adobe/CAD, etc?
Yes, depending on the specifications. You generally need a powerful thin client to run applications like Adobe, CAD, etc.
8. How to update the firmware of your thin client?
You can update the firmware of your thin client using the remote management tool provided with your thin client. Click here to see how a powerful remote management tool looks like.
9. Can I increase the ROM of my thin client?
You cannot increase the ROM of your thin client as thin clients only have flash memory. This flash memory will be used just for the thin client software and the mechanism to boot the OS; all of the remaining computing resources will be present on the server. Technically, there’s no point of increasing the ROM as all the data that you save will be stored on the server and not locally.
10. Does a thin client computer typically have a hard disk?
Thin clients do not have hard disk, they only have flash memory.
11. How to build a cheap thin client?
It is not recommended to build a thin client by yourself if you want to use it to access remote environments in secure conditions. Despite its apparent simplicity, it involves many components and complex technologies which needs to be dealt by the professionals. The management tool in particular requires years of development from specialized editors.
12. How does a thin client differ from a regular computer?
Thin clients differ from regular computers in the way that they operate. A thin client is run by the computing resources present on the remote server, whereas a regular computer runs by the computing resources present locally on the system.
13. What is the difference between thick client & thin client architectures? 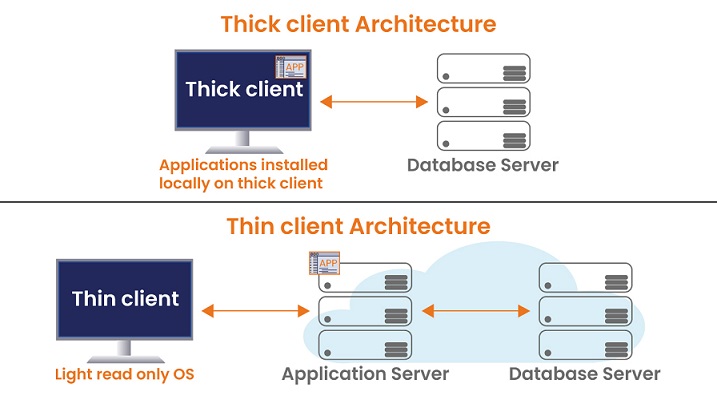
14. When should a company consider a thin client IT setup?
If the number of employees present in your company are around 10 people, then it is relatively easy for your IT administrator to manage the company devices. Management of devices includes regular software updates, checking anti-virus, troubleshooting, security updates, control of Shadow IT, etc. But as the number of employees increases, all this becomes very difficult to manage since the administrator has to manage each endpoint one by one. Considering a thin client setup increases the security of your endpoints & simplifies the management of your endpoints as you can manage them remotely from anywhere. Learn more about thin client benefits in this blog.
15. Why should a company consider thin client over thick client?
A company could consider thin clients over thick clients for the following reasons:
- More secure
- Tuned for accessing virtual workspaces
- Easier to manage
- 10 times less power consumption compared to a PC
- Longer life span (6 to 10 years)
- No anti-virus costs
- Great TCO & ROI
- Less software updates
- Completely silent (as thin clients do not have a fan)
16. Can thin client work without a server?
Thin clients cannot work without a server. Thin client only has OS locally and all the computing resources are present on the server. This server can be a cloud provider.
If you have more specific questions about thin clients or if you are considering a thin client project, feel free to contact us.
Tags In
Search
Recent posts
- The main Cybersecurity risks of remote work: Safeguarding your infrastructure in a connected world 3 April 2024
- Introducing the latest version of ZeeScan! 22 February 2024
- Chromebooks in Business: Advantages and Challenges to Consider 19 February 2024
- Happy New Year from all of us at ZeeTim! 1 January 2024
- ZeeTim’s 2023 recap: Elevating end-user computing excellence 26 December 2023




